Chemistry
Tunneling driven dynamics for the PD3 group of the octyl phosphonium cation in an ionic liquid has been observed by means of solid-state NMR spectroscopy. Deuteron line-shape analysis and relaxation time measurements provide information about the structure, mobility and rearrangements of the cations in the solid, supercooled and liquid states. Hydrogen bonds of different strengths allow the change in molecular ordering upon phase transformation to be mapped. More information can be found in the Research Article by D. I. Kolokolov, R. Ludwig et al. (Cover Feature)
ChemPhysChem
The Front Cover illustrates the isotope effects for the protic ionic liquid (PIL) triethylammonium methanesulfonate as explored by deuterium solid-state NMR spectroscopy. The 2H NMR line shape analysis provides deuteron quadrupole coupling constants, which are sensitive for hydrogen bonding and allow probing the characteristics of a broad heterogeneous phase. More information can be found in the Research Article by Daniil I. Kolokolov, Ralf Ludwig and co-workers. (Front Cover)
ChemPhysChem
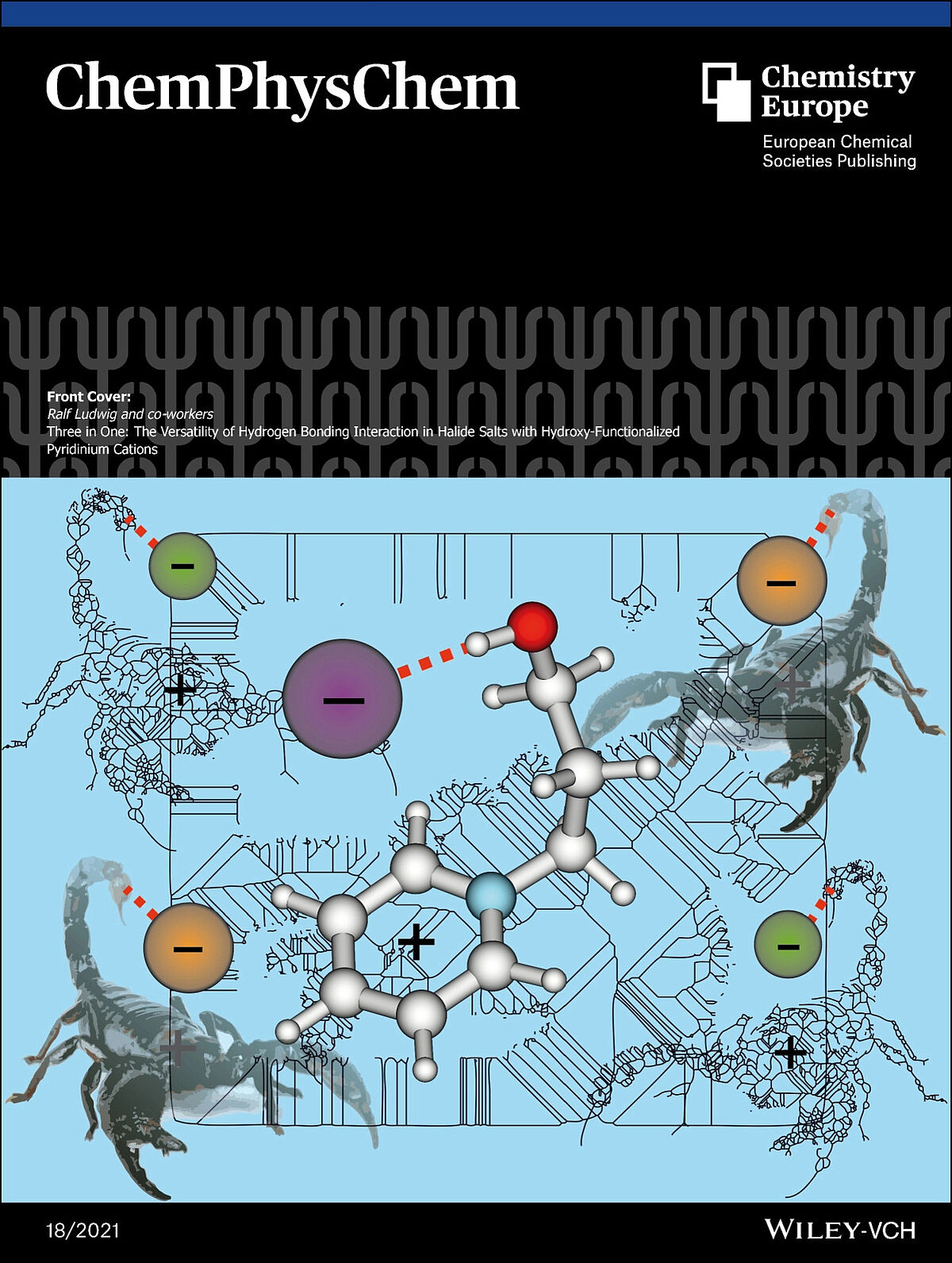
The Front Cover shows one of the three types of hydrogen bonding observed in hydroxy-functionalized halide salts. Here, the halide anion forms a hydrogen bond to the hydroxy group and interacts with the ring system of the cation at the same time. The versatility of structures demonstrates the importance of non-covalent interactions, in particular the role of hydrogen bonding. (Front Cover)
ChemPhysChem, 22, 1850-1856, 2021
Chem. Methods
The Cover Feature shows that the spectroelectrochemical methods simultaneously record spectral and electrochemical data that often contain more chemical information than can be conveniently analysed. In this work, we present a method for the extraction of individual chemical signatures from single-run spectroelectrochemical measurements. In combination with computational chemistry, this new approach will likely be helpful to better understand the electrochemistry of a wide range of molecular complexes. The cover was designed by J. J. Wending. More information can be found in the full paper by Benedict J. Elvers et al. (Cover Feature)
ChemPhysChem
This work nicely shows that attractive local and directional interactions such as hydrogen bonds are able to overcome repulsive long-range and undirected interactions. In the future, we want to show that by forming clusters of ions with like charge, we can control the properties of ionic liquids, such as viscosity, conductivity or phase behavior. (Front Cover)
ChemPhysChem, 2020, Volume 21, Issue 21
Angewandte Chemie
The secrets of ionic liquids' properties rely on the delicate balance between Caoulomb interaction, hydrogen bonding and dispersion forces. In their Communication on page 8589 ff. S. P. Verevkin, R. Ludwig et al. show how these different types of interactions contribute to vaporization enthalpies. For the detailed analysis, exclusively experimental methods and a well-suited set of ionic and molecular liquids were used. (Inside Back Cover)
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics
This paper reports quantum chemical calculations of the kinetic and thermodynamic stability of cationic dimers. With increasing akly chain lenght, cooperative hydrogen bonds overcome the repulsive Coulomb forces. The cationic dimers with longer alkyl chains should be observable in gas phase experiments at low temperatures.
Chemistry a European Journal
Understanding the mechanism of photocatalytic water reduction is essential for the development of effective catalysts. A new, self‐assembling, and sulfur‐free [FeFe]‐hydrogenase mimic, which shows good catalytic activity, is described. The action of the visible‐light‐driven iron catalyst within the cycle of H2 production from water is monitored by a combination of in‐situ spectroscopic methods. More information can be found in the Full Paper by R. Ludwig et al.
ChemPhysChem
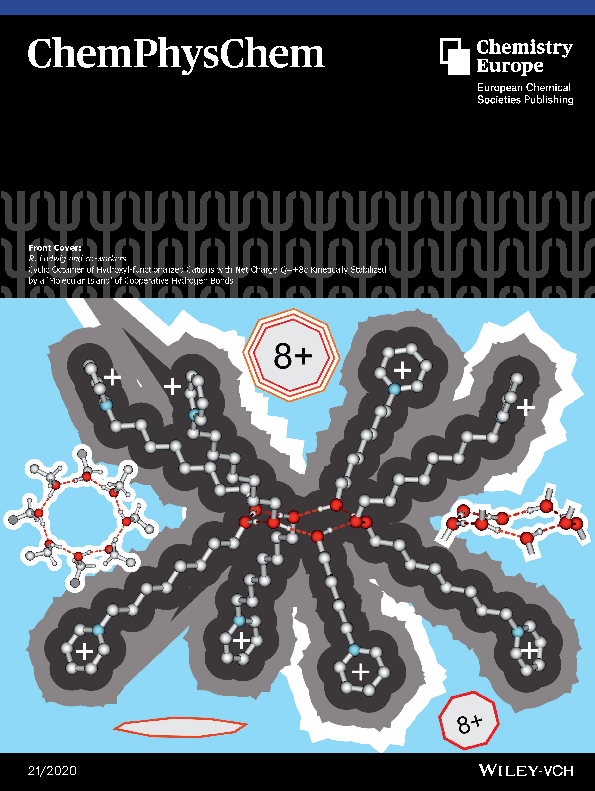
The Cover Feature visualizes how hydrogen bonding can overcome Coulomb repulsion in clusters of like‐charged ions. In their communication Ludwig et al. report kinetically stable cationic clusters with a high net charge up to Q=+6e. Despite strongly repulsive Coulomb forces, the hydroxy‐functionalized N‐(3‐hydroxypropyl)pyridinium cations are trapped by hydrogen bonding in a cyclic hexamer.
Chemical Communications
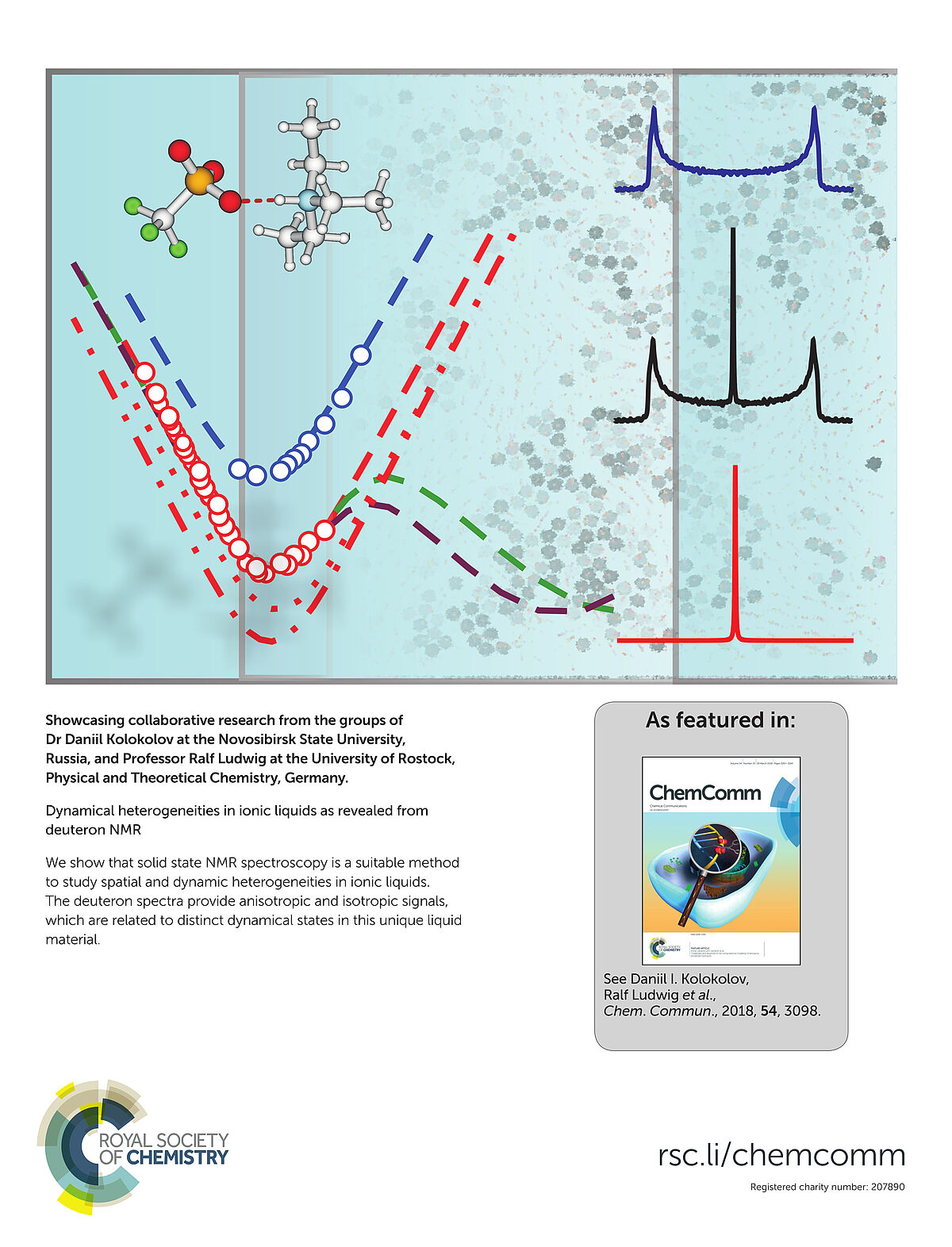
We show that solid state NMR spectroscopy is a suitable method to study spatial and dynamic heterogeneities in ionic liquids. The deuteron spectra provide anisotropic and isotropic signals, which are related to distinct dynamical states in this unique liquid material. (Inside Back Cover)
Angewandte Chemie
Hydrogen bonds between ions are identified by the first deuteron quadrupole coupling constants (DQCCs) for protic ionic liquids (PILs), measured by solid-state NMR spectroscopy. In their Communication (DOI: 10.1002/anie.201708340) D. I. Kolokolov R. Ludwig, et al. show that this NMR parameter is a sensitive probe of the doubly ionic hydrogen bonds present in PILs. The picture shows the NMR spectra as bridges symbolizing the doubly ionic hydrogen bonds between oppositely charged ions in PILs and mimicking the rocky mountains in the background.
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics
This paper reports the calculation of the kinetic and thermodynamic stability of cation clusters with added molecules or counterions. These clusters of like-charged ions are stabilized by cooperative hydrogen bonding between hydroxyl groups overcoming the repulsive Coulomb forces. The cationic clusters show characteristic spectroscopic properties and some of them should be observable in demanding gas phase experiments.(Backsidecover)
Chemie konkret
Das Foto zeigt ein oktaedrisches THF-Clathrat-Hydrat mit Schulter. Im Beitrag auf S. 59 wird gezeigt, wie sich solche THF-Clathrat-Hydrate mit einfachen Mitteln in einer Unterrichtsstunde herstellen lassen. Methanhydrate können als potentielle fossile Energielieferanten im Unterricht thematisiert werden und Einblicke in ein aktuelles und nicht abgeschlossenes Forschungsthema geben.(Cover)
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics
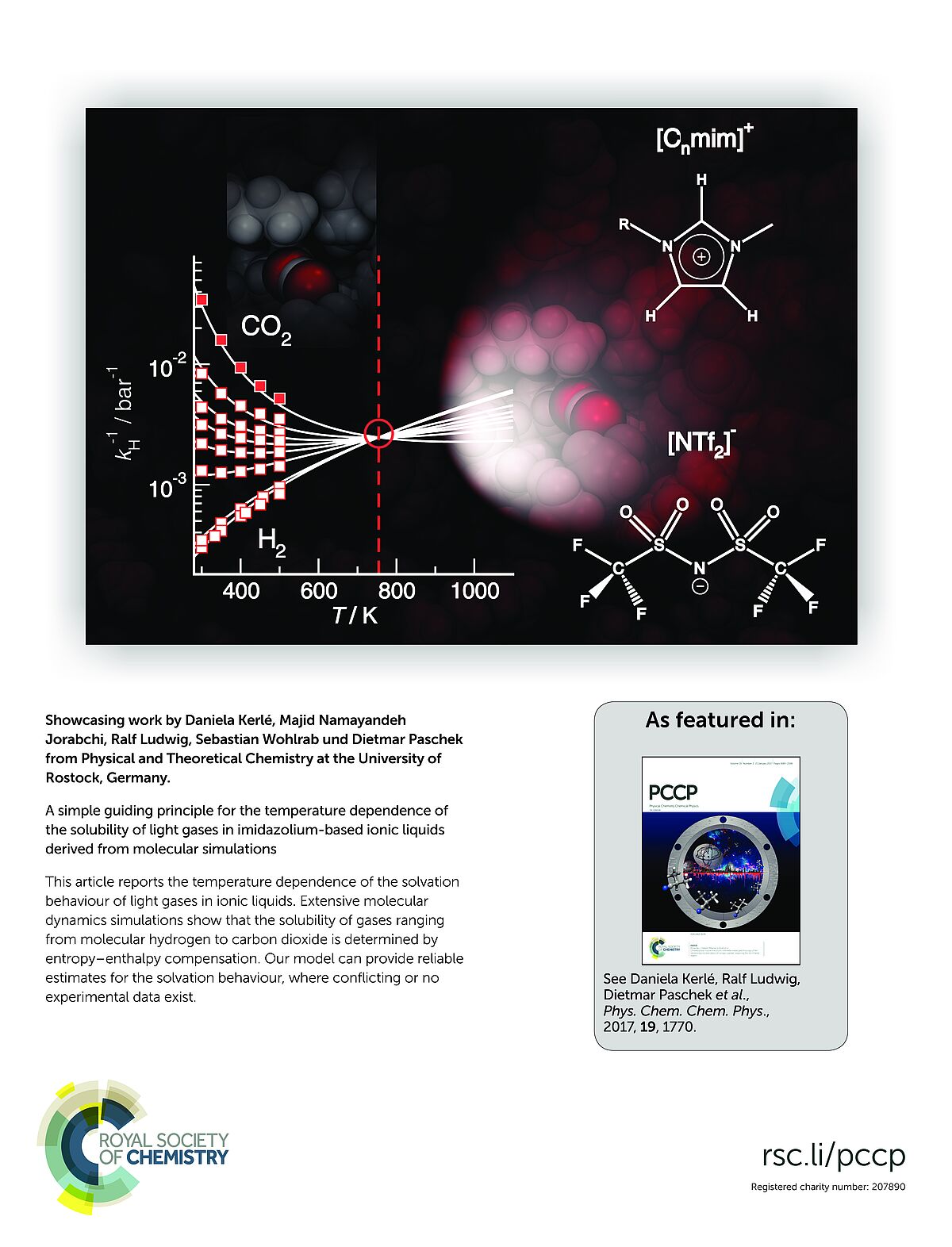
This article reports the temperature dependence of the solvation behaviour of light gases in ionic liquids. Extensive molecular dynamics simulations show that the solubility of gases ranging from molecular hydrogen to carbon dioxide is determined by entropy–enthalpy compensation. Our model can provide reliable estimates for the solvation behaviour, where conflicting or no experimental data exist. (Insidecover)
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics
Ludwig et al. describe a method for the accurate determination of deuteron quadrupole coupling constants and reorientational correlation times in protic ionic liquids by means of NMR relaxations time experiments, DFT-calculations and molecular dynamics simulations. (Frontcover)
ChemPhysChem
Cyclic tetramer of hydrogen-bonded cations in the 1-(2-hydroxyethyl)-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate ionic liquid. Weinhold, Ludwig et al. could assign the observed vibrational modes in the infrared spectra to DFT-calculated frequencies of clusters of like-charged ions. More information can be found in the Cummunication by F. Weinhold, R. Ludwig et al. on page 458 in Issue 4, 2016 (Frontcover)
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics
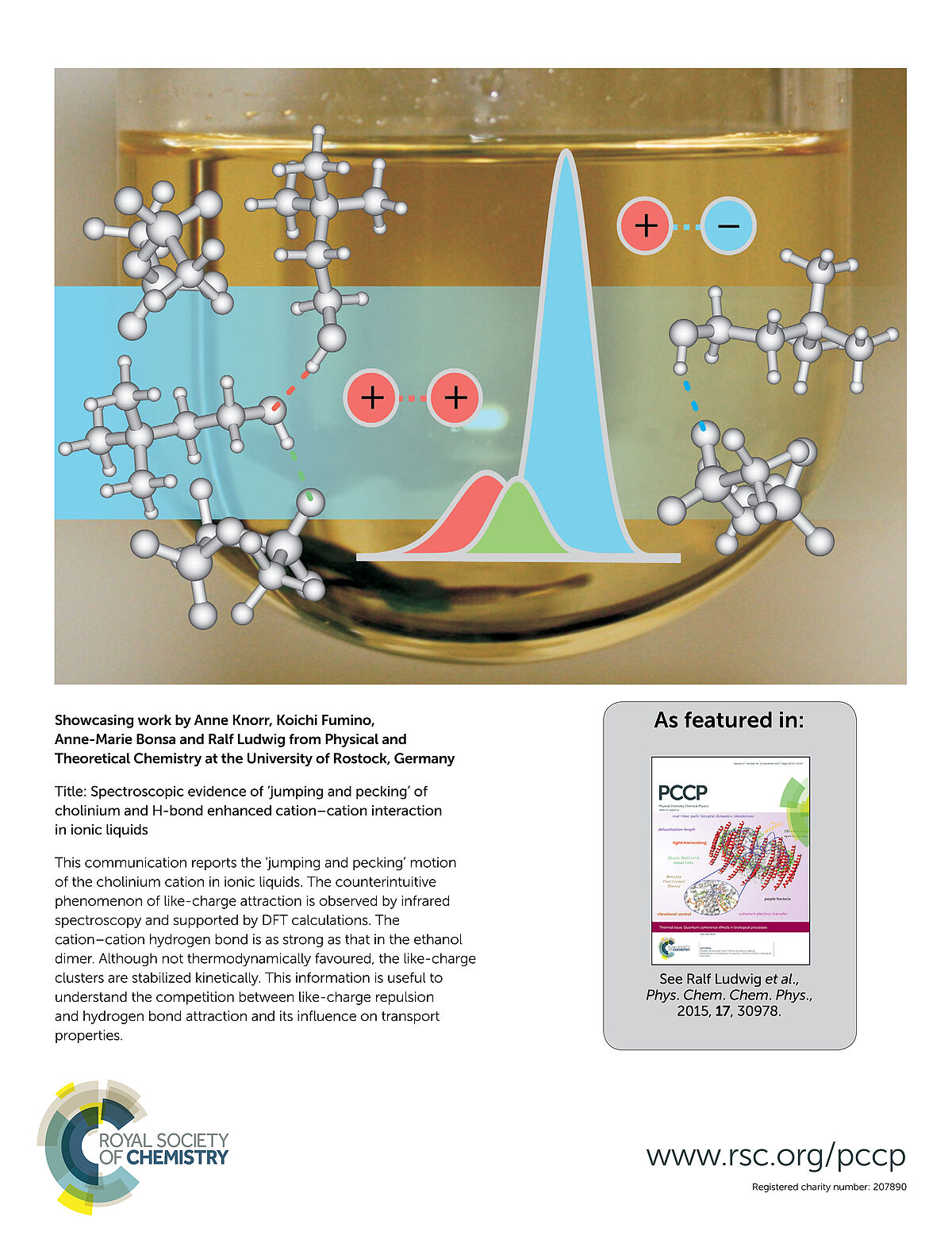
This communication reports the ‘jumping and pecking’ motion of the cholinium cation in ionic liquids. The counterintuitive phenomenon of like-charge attraction is observed by infrared spectroscopy and supported by DFT calculations. The cation–cation hydrogen bond is as strong as that in the ethanol dimer. Although not thermodynamically favoured, the like-charge clusters are stabilized kinetically. This information is useful to understand the competition between like-charge repulsion and hydrogen bond attraction and its infl uence on transport properties. (Backsidecover)
ChemPhysChem
Hydrogen bonding governs the vibrational dephasing in ionic liquids. Time-resolved coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering (CARS) and theoretical studies show that this process takes place on the fs-to-ps timescale. More information can be found in the Full Paper by R. Ludwig, S. Lochbrunner, O. Kühn et al. on p. 2519. (Backsidecover)
ChemPhysChem, 2015, Volume 16, Issue 12
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics
This communication reports the competition between hydrogen bonding and dispersion interaction in protic ionic liquids. It is shown that dispersion forces can be as strong as hydrogen bonds and that they influence vibrational frequencies in the far infrared to different extents. This information is useful to understand the subtle balance between Coulomb interaction, hydrogen bonding and dispersion forces and the effect on the properties of these Coulomb dominated systems. (Backsidecover)
Angewandte Chemie
The secrets of ionic liquid properties rely on the subtle energy balance between Coulomb interaction, hydrogen bonding, and dispersion forces. In their Communication, R. Ludwig et al. show that far-infrared spectroscopy is suitable to study the competition between hydrogen bonding and dispersion interactions in these Coulomb-dominated liquids. Characteristic spectral signatures allow the transition between both types of noncovalently bound “ion pairs” to be quantified. (Insidecover)
ACS Catalysis
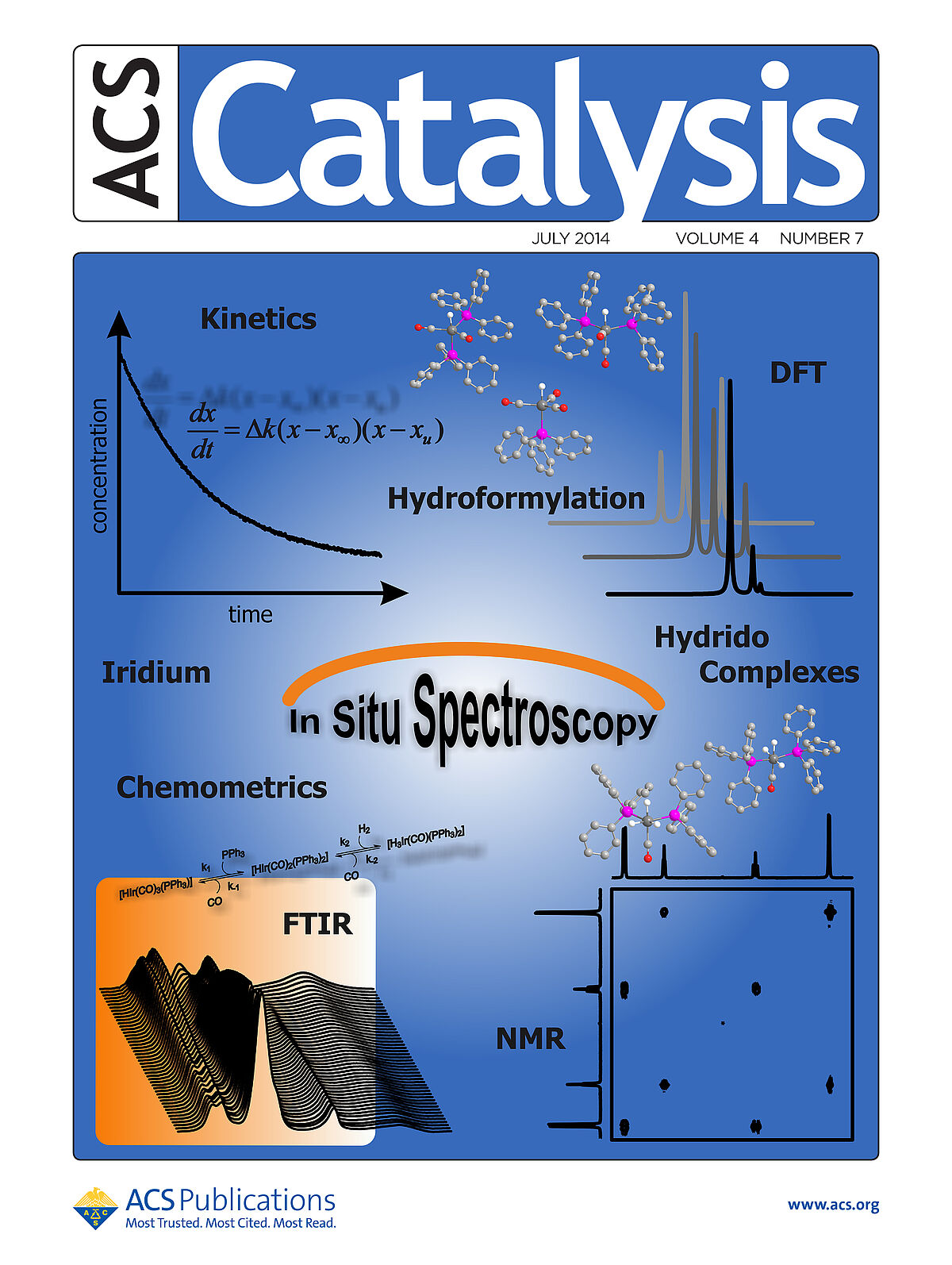
In situ spectroscopic investigations on homogeneous iridium catalysts for the hydroformylation of olefins. HP-FTIR and NMR spectroscopy have been applied for the characterization and quantification of an equilibrium mixture of iridium hydrido complexes. Spectroscopic data were analyzed by chemometric methods, and FTIR spectra have been compared with calculated spectra obtained by DFT methods.(Frontcover)
Chemistry A European Journal
Happy birthday, ethylammonium nitrate! The first widely known ionic liquid, studied by Paul Walden, turns 100 years old. Some important properties of EAN have been addressed properly for the first time. In their Communication on page 11640 ff., R. Ludwig, S. Verevkin et al. show that ethylammonium nitrate evaporates as contact-ion pairs at low temperatures (<419 K). Above that temperature, neutral molecules dominate over ion pairs, resulting in the relatively low boiling point of 513 K.(Insidecover)
ChemPhysChem
On p. 3102 ff., Ludwig et al. report infrared measurements on trace amounts of water dissolved in ionic liquids. Using water as a sensitive probe they show that ionic liquids can be more hydrophobic than molecular liquids. This is a surprising result, given that the liquid material consists solely of ions. (Insidecover)
Angewandte Chemie
Understanding the mechanism of photocatalytic water splitting is essential for the development of effective catalysts beyond trial and error. In their Communication R. Ludwig, M. Beller, A. Brückner et al. monitored the simultaneous action of iridium and iron catalysts within the cycle of H2 production from water by a combination of three in situ spectroscopic methods and thus verified the reaction mechanism.(Backsidecover)
ChemCatChem
The rhodium-catalyzed hydroformylation of 3,3-dimethyl-1-butene is monitored by in situ, high-pressure FTIR spectroscopy, as pictured, giving time-dependent concentration profiles of organic components and metal-organic reaction intermediates. In their paper on page 287 ff., Selent et al. offer an improved perception of mono- and diphosphite-modified catalysis. (Insidecover)
ChemPhysChem
The cover picture shows water molecules in different hydration shells at the surface of the model protein ubiquitin. The properties of proteins and the role of solvent in conformational dynamics is a central topic to the DFG-Foschergruppe (FOR 436) which forms the basis of this special issue. The polymorphism, dynamics and function of water at molecular interfaces is discussed with contributions from R. Winter (p. 2715, 2779), Ludwig (p. 2722, 2731), Geiger and Paschek (p. 2722, 2737, 2742), Brovchenko (p. 2660, 2695), Tolan (p. 2809), Marx (p. 2703, 2751, 2759), and Weingärtner (p. 2794, 2802). (Frontcover)
ChemPhysChem
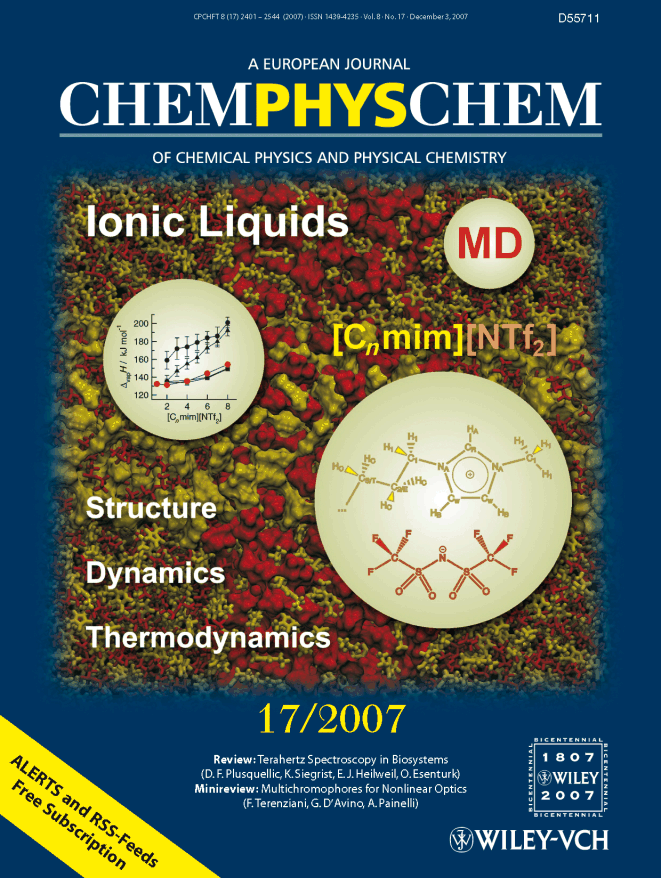
The cover picture shows a snapshot from a molecular dynamics (MD) simulation of the nanostructured ionic liquid [C2mim][NTf2]. In their article on page 2464 Köddermann et al. have developed an atomic-detail molecular force field for ionic liquids of type [Cnmim][NTf2] (n=2,4,6,8). This is the first time such a model is capable of correctly describing structural, dynamical and thermodynamical properties of these ionic liquids over a wide temperature range.. (Frontcover)